Welding service
Metal welding service is a process of joining metal parts by melting and fusing them, creating a permanent, strong bond. Key types include MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, known for speed and versatility; TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, valued for precision; and laser welding, ideal for intricate work. Welding is widely used in automotive frames, aerospace components, pipelines, and construction beams. Specific applications include car chassis, aircraft fuselages, fuel tanks, and steel frameworks for buildings.
Custom Metal Welding Services| Professional OEM Factory
Xinjiuxinji specializes in providing custom metal welding services, equipped to handle projects of any size—from intricate, small-scale parts to large, complex structures. Our factory utilizes advanced welding techniques, including MIG, TIG, and laser welding, to ensure that each product meets the highest standards of precision, durability, and strength. We pride ourselves on stringent quality control and meticulous attention to detail, ensuring consistent, reliable results across every project.
Professional Welding Line|Flexible And Optimized Welding Solutions
As a specialized metal processing supplier, we offer several types of metal welding, each suited to specific applications and requirements. Here’s an overview of common welding types, how each works, and their unique advantages:
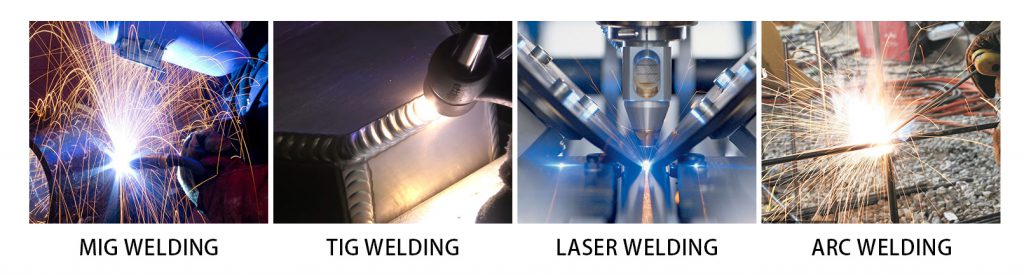
- MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas)
How it Works: MIG welding uses a continuous wire feed as an electrode, which melts and joins the metals under a shielding gas to prevent contamination.
Advantages: Known for its speed and ease of use, MIG welding provides clean welds with minimal splatter, making it ideal for high-volume production.
Applications: Commonly used for automotive frames, general fabrication, and large assemblies where speed and efficiency are prioritized. - TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas)
How it Works: TIG welding uses a tungsten electrode with a shielding gas to create precise, controlled welds. The process requires skill but results in high-quality, clean welds.
Advantages: Offers excellent precision and is ideal for thin metals or intricate designs, providing high strength with minimal distortion.
Applications: Preferred in aerospace, medical equipment, and decorative items where precision, aesthetics, and strength are essential. - Laser Welding
How it Works: Laser welding uses a focused laser beam to join materials with extreme accuracy. The concentrated heat allows for fast welding with minimal heat-affected zones.
Advantages: Ideal for small, delicate components or high-precision requirements, producing clean welds with little post-processing needed.
Applications: Used in electronics, fine jewelry, and medical devices, as well as in industries requiring micro-welding or complex joints. - Arc Welding
How it Works: Arc welding uses an electric arc to melt metals and a filler material, creating strong joints. This method is versatile and suitable for thick metals.
Advantages: Cost-effective and suitable for outdoor use, arc welding provides strong bonds, even in demanding environments.
Applications: Often used in construction, pipelines, and heavy machinery manufacturing where durability and strength are crucial.
Each welding type brings unique strengths, allowing us to match the best method to your project’s require
Precision Metal Welding: Guaranteeing Delivery Time and Quality
As a professional metalworking supplier specializing in metal welding, here’s an overview of the typical steps involved in producing a welded metal part. A welding project generally includes several key stages to ensure quality, precision, and adherence to client specifications:
- Design and Planning
In this initial phase, we work closely with the client to determine part specifications, including dimensions, material requirements, and any specific welding needs. Detailed drawings and CAD models are created to visualize the end product. - Material Selection and Preparation
Based on the design, we select the appropriate metal type (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum). The material is then cut, cleaned, and prepped to ensure high-quality welds free from contaminants. - Fixture Setup
Custom fixtures or jigs are prepared to hold the components securely in place. This setup ensures precise alignment and reduces warping or shifting during the welding process. - Welding Process
The core step, using techniques such as MIG, TIG, or laser welding. During welding, our skilled technicians carefully control heat and speed to achieve strong, clean welds and avoid distortion. - Inspection and Testing
After welding, each part undergoes thorough inspection for structural integrity and dimensional accuracy. Tests may include visual checks, ultrasonic testing, or X-rays for high-stress components. - Finishing and Surface Treatment
To enhance appearance and durability, parts may go through finishing processes like grinding, polishing, or coating, ensuring they meet both functional and aesthetic standards.
These steps ensure every welded component produced meets exact specifications, highlighting Xinjiuxinji’s commitment to quality and precision.






 +86 18892239158
+86 18892239158










